The Bifurcation of AI: Diverging Paths Between China and the Global Market
The artificial intelligence (AI) landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, marked by the emergence of two distinct technological ecosystems. On one side is China, rapidly advancing its AI capabilities through domestically developed hardware and software, spearheaded by companies like Huawei and DeepSeek. On the other side is the global market, heavily reliant on established industry leaders such as Nvidia, AMD, and other Western semiconductor firms. This divergence is not merely technological but deeply rooted in geopolitical, economic, and strategic imperatives, creating a bifurcation that could shape the future of AI for decades to come.
At the heart of this bifurcation lies the growing decoupling between China and the rest of the world, driven by escalating trade tensions, export controls, and national security concerns. The United States, along with its allies, has imposed stringent restrictions on the export of advanced semiconductor technologies to China. These measures aim to limit China’s access to cutting-edge AI chips, such as Nvidia’s A100 and H100 GPUs, which are critical for training large-scale AI models. In response, China has accelerated its efforts to achieve technological self-sufficiency, investing heavily in domestic semiconductor development, AI algorithms, and high-performance computing infrastructure.
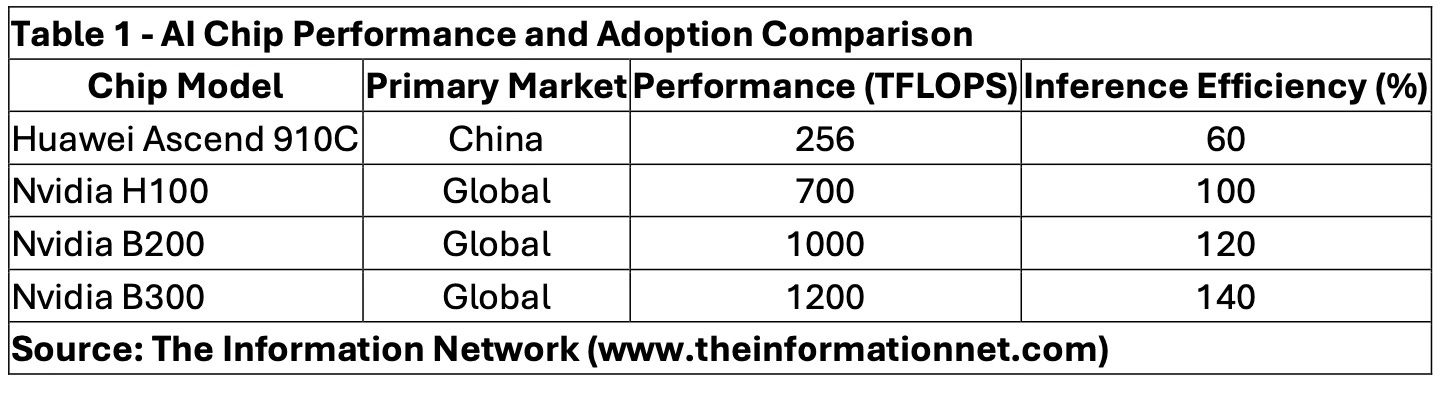
China’s strategy revolves around building an indigenous AI ecosystem that can compete globally without relying on Western technologies. Huawei’s Ascend series of AI processors, particularly the Ascend 910C, represents a cornerstone of this strategy. Despite offering around 60% of the inference performance of Nvidia’s H100, the Ascend 910C is being rapidly adopted within China’s AI industry, including by firms like DeepSeek. This move is not just about performance but about securing supply chains and reducing vulnerabilities to foreign sanctions.
Table 1 compares the performance and adoption of AI chips from Huawei and Nvidia, highlighting key differences in their target markets, processing power, and efficiency. It illustrates how Huawei’s Ascend chips are gaining traction in China while Nvidia continues to dominate global markets with superior performance, reinforcing the bifurcation in AI hardware ecosystems.
Meanwhile, the global market continues to thrive on Nvidia’s dominance in AI hardware. Nvidia’s GPUs are considered the gold standard for AI training and inference, powering everything from data centers to autonomous vehicles. The introduction of new architectures like Blackwell (B200) and the upcoming B300 promises to further solidify Nvidia’s leadership, offering unprecedented performance improvements and energy efficiency. However, the global reliance on Nvidia and similar Western firms also exposes supply chain risks, particularly in the face of geopolitical disruptions.
This technological bifurcation is also reflected in the software domain. China is fostering the development of AI models and frameworks that are optimized for domestic hardware, while global AI research continues to evolve around open-source platforms and Nvidia’s CUDA ecosystem. The divergence extends to data governance, with China implementing strict data localization laws, contrasting with the more open data-sharing practices prevalent in Western AI development.
The implications of this bifurcation are profound. It could lead to the emergence of parallel AI ecosystems with limited interoperability, affecting everything from global supply chains to cybersecurity. Companies operating in both markets may face increased costs and complexity, needing to develop separate AI solutions tailored to each ecosystem. Moreover, the competitive dynamics of the AI industry could shift, as China’s push for self-reliance accelerates innovation within its borders, potentially challenging the technological supremacy of Western firms in the long run.
In conclusion, the bifurcation of AI is not just a technological phenomenon but a reflection of the broader geopolitical realignment. It underscores the strategic importance of AI as a driver of economic growth, national security, and global influence. As this divide deepens, it will shape the future trajectory of AI development, adoption, and regulation across the world.
Strategic Technologies: Huawei Ascend vs. Nvidia GPUs
The divergence between China’s AI ecosystem and the global market is prominently reflected in the technological strategies of key players, particularly Huawei and Nvidia. Huawei’s Ascend chips are designed to reduce reliance on U.S. technology, capitalizing on China’s domestic semiconductor advancements. In contrast, Nvidia continues to dominate globally with its high-performance GPUs, especially in AI training workloads.
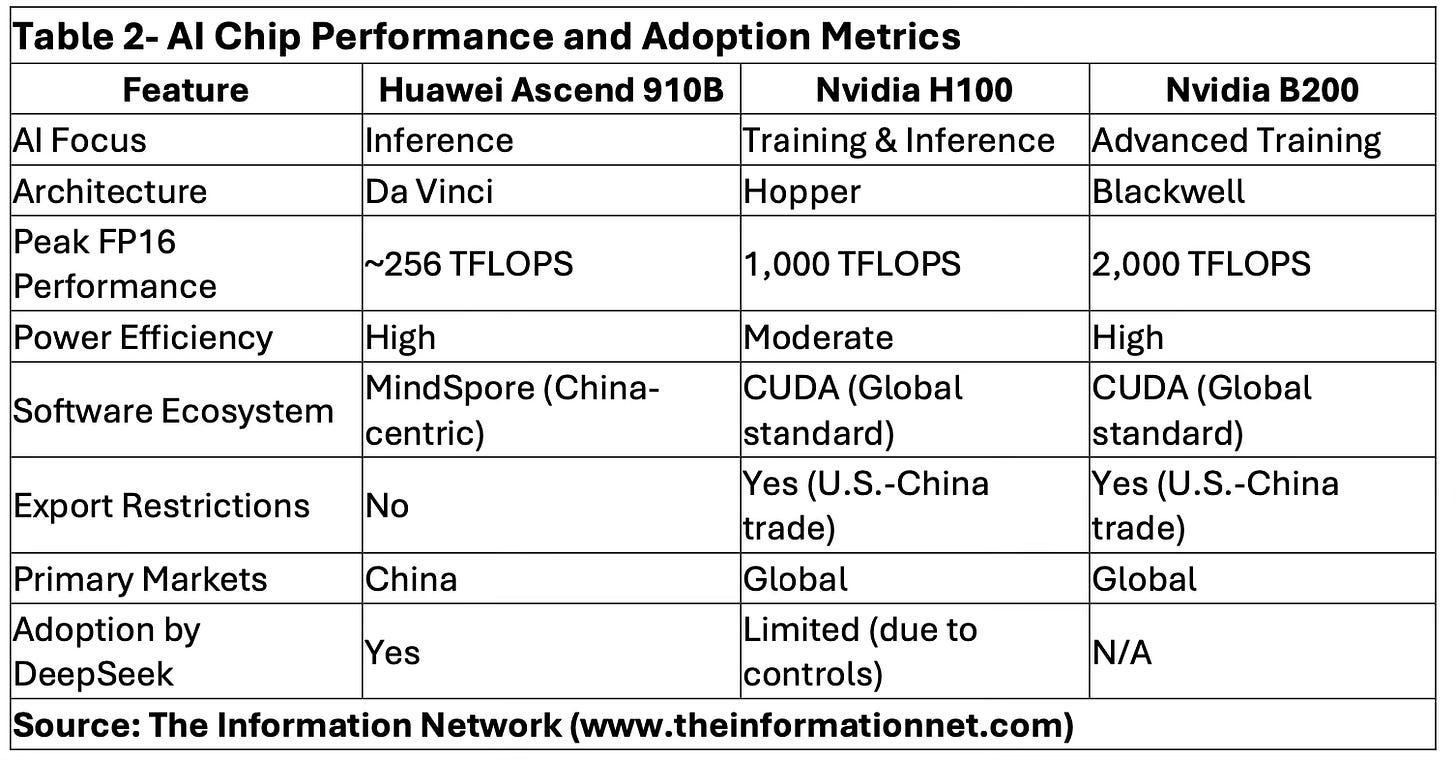
Huawei’s Ascend series, including the Ascend 910B, is optimized for AI inference tasks and aligns with China’s push for self-sufficiency. Its focus on energy efficiency and integration within Chinese tech stacks makes it a preferred choice for domestic firms like DeepSeek. Meanwhile, Nvidia’s H100 and B200 GPUs remain the gold standard for AI training, favored for their superior processing power and support from robust global software ecosystems like CUDA.
However, Nvidia faces regulatory hurdles in China, with export restrictions limiting the availability of its most advanced chips. This has provided an opening for Huawei to capture market share domestically. The technological gap is narrowing, but Nvidia maintains a performance edge in high-compute applications, particularly in large language model (LLM) training.
Table 2 provides a detailed comparison of AI chips used for training and inference, focusing on Huawei’s Ascend 910B and Nvidia’s H100 and B200. It showcases critical differences in architecture, power efficiency, and software ecosystems, emphasizing how geopolitical restrictions influence adoption patterns, particularly for companies like DeepSeek operating in both China and global markets.
Huawei’s progress with Ascend chips illustrates China’s commitment to building an independent AI hardware ecosystem. While Nvidia’s GPUs outperform Huawei’s in raw compute power, especially for large-scale AI model training, the bifurcation is driven as much by geopolitics as by technology. Chinese firms like DeepSeek are adapting quickly, leveraging Huawei’s chips where Nvidia’s are restricted, creating two parallel AI development tracks.