The Impact of China’s Ban on Intel: How U.S. Sanctions Backfired and Contributed to Intel’s Troubles
For decades, Intel has stood as a beacon of U.S. semiconductor dominance. But in 2024, the unintended consequences of U.S. sanctions against China highlighted just how fragile that position has become. Designed to cripple China’s semiconductor industry, these sanctions instead backfired, propelling Chinese chipmaking to new heights while simultaneously exacerbating Intel’s internal struggles. China’s retaliatory ban on Intel’s processors only deepened the company’s woes, ultimately contributing to the ouster of CEO Pat Gelsinger and reshaping the competitive dynamics of the global semiconductor industry.
The Retaliatory Ban: A Turning Point for Intel
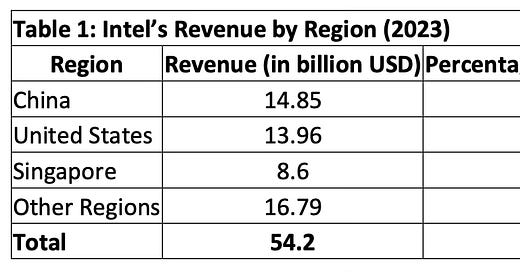
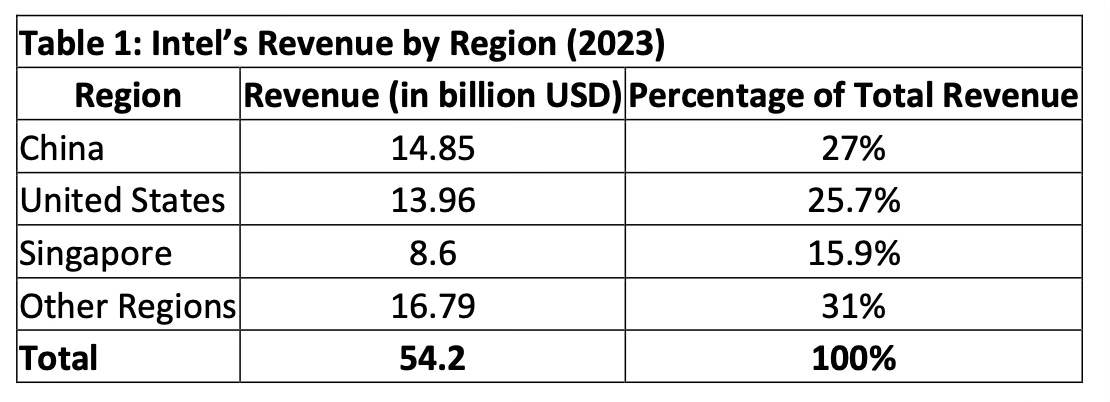
In early 2024, China banned Intel from selling its processors for use in government systems, citing national security concerns. This was a clear retaliation against U.S. export controls aimed at restricting China’s access to advanced semiconductor manufacturing tools and cutting-edge technologies. For Intel, this ban was more than just a political statement—it was a financial blow. China accounted for 27% of Intel’s $54 billion in annual revenue, making it one of the company’s largest markets.
The ban’s impact was immediate and significant, forcing Chinese companies to shift to domestic suppliers like Loongson and Phytium. These Chinese firms, long overshadowed by Intel’s dominance, seized the opportunity to expand their market share. For Intel, the loss of the Chinese government sector further strained its already precarious position in the global semiconductor hierarchy.
The following table underscores the importance of the Chinese market to Intel. With China contributing $14.85 billion to Intel’s revenue in 2023, the scale of the financial damage becomes clear.
How U.S. Sanctions Strengthened China
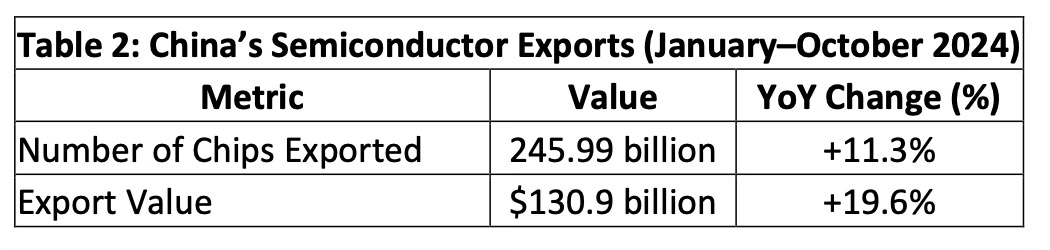
The irony of the U.S. sanctions lies in their unintended consequences. Instead of stifling China’s semiconductor ambitions, they galvanized the country’s chipmaking industry. Between January and October 2024, China exported 245.99 billion chips, an 11.3% year-over-year increase. The value of these exports rose by 19.6% to $130.9 billion.
The table below illustrates this rapid growth. China’s ability to increase both the volume and value of its chip exports demonstrates its resilience and strategic response to external pressures.
But it wasn’t just exports. Domestic production surged as well,