In this article I am making it available to all subscribers, free and paid. So there is no Paywall. This will hopefully make free subscribers aware of the depth and breadth of my articles.
Background of my Coverage of TSMC
I’ve been positive about TSMC in every one of my articles on the company going back a number of years. A list of articles for just for 2023 and 2024 is shown below.
A list of these articles by title and hyperlink and written for Seeking Alpha are:
TSMC Raising Prices 8.7% In 2024 As Revenue Growth (March 5, 2024)
TSMC's Market Dominance Targeted By Intel By 2025 (January 17, 2024)
Taiwan Semiconductor Makes Chips For 3 Of The Top 4 (September 26, 2023)
Taiwan Semiconductor: Significantly Undervalued As Chip (August 16, 2023)
TSMC Is Expanding Its Global Production Footprint (April 4, 2023)
Tracking A Trailing-Edge Semiconductor Slowdown (May 10, 2024)
TSMC: My Top Pick In 2023 As It Dominates Samsung Electronics And Intel Foundries (January 9, 2023)
Since August I’ve been writing for Substack, as shown in the following article -
Taiwan Semiconductor - Dominating AI Chip and Package Production (August 18, 2024)
My top pick articles:
TSMC has been my top semiconductor company throughout my writings, and in my January 10, 2020 article below I detailed why it was my top pick for the year. Taiwan Semiconductor: My Top Semiconductor Pick For 2020 (January 10, 2020)
I repeated this in 2023 in my article - TSMC: My Top Pick In 2023 As It Dominates Samsung Electronics And Intel Foundries (January 9, 2023)
Key Takeaways from TSMC's Q3 2024 Earnings Call:
These takeaways set the tone for this article, illustrating TSMC's strong operational performance and growth outlook, and providing the investor with a clear view of why TSMC is outperforming its competitors, Intel and Samsung.
Strong Revenue Growth: TSMC reported $23.5 billion in Q3 2024 revenue, a 12.8% sequential increase driven by robust demand for 3nm and 5nm technologies. AI-related demand and strong smartphone sales were primary contributors, with advanced technologies accounting for 69% of total wafer revenue.
Gross Margin Surge: Gross margin increased to 57.8%, exceeding expectations by 230 basis points. This improvement was attributed to a higher capacity utilization rate and cost-efficiency gains. For Q4 2024, TSMC expects its gross margin to further rise to between 57% and 59%.
Rising AI Demand: TSMC observed “insane” demand for AI chips, with AI-related revenues expected to triple in 2024, making up a mid-teen percentage of total revenue. This rapid growth is driven by customers in high-performance computing (HPC), AI accelerators, and data center processors.
CapEx and Expansion Plans: TSMC reaffirmed its 2024 CapEx forecast of over $30 billion, with 70-80% dedicated to advanced process technologies. TSMC's aggressive investment is aimed at supporting future demand for AI and 3nm chips, with a strong focus on ramping up 2nm technology in coming years.
Profitability Outlook: For Q4 2024, TSMC expects revenue to rise further to between $26.1 billion and $26.9 billion, reflecting a 13% sequential increase. Continued strong demand for 3nm and 5nm processes, especially in AI and smartphone segments, will drive further profitability, with an anticipated operating margin between 46.5% and 48.5%.
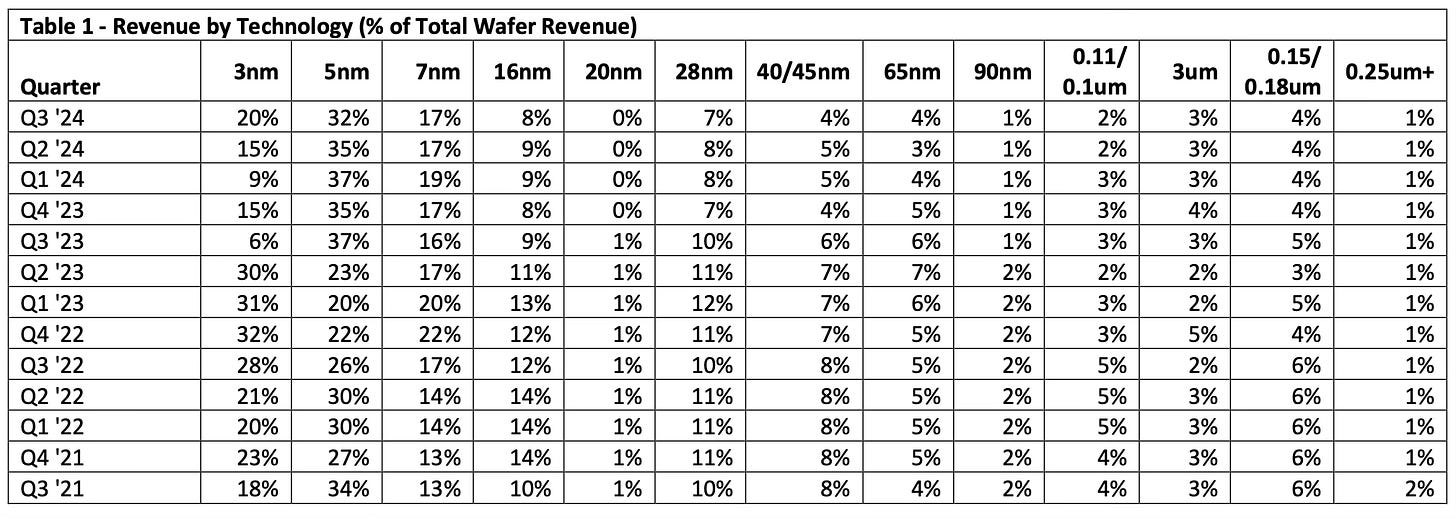
Revenue Growing at the 3nm Node
Following its Q3 2024 earnings call, TSMC has once again shown why it leads the global semiconductor foundry market. With exceptional growth fueled by its cutting-edge 3nm and 5nm nodes, TSMC continues to distance itself from competitors Intel and Samsung. While both Intel and Samsung struggle with delays and yield issues in advanced technologies, TSMC’s rapid scaling and focus on AI-driven demand have proven a winning formula.
TSMC's total Q3 revenue of $23.5 billion was driven by advanced technologies, with 3nm contributing 20% and 5nm 32% to the total wafer revenue, as shown in Table 1. In comparison, Intel reported $14.2 billion in Q3 revenue, with significant delays in its 4nm and 3nm nodes, and Samsung's foundry segment generated just $5.8 billion, plagued by yield issues in its 3nm process. TSMC’s consistent ability to ramp production of cutting-edge nodes while maintaining high yields sets it far ahead of its competitors.
While Intel and Samsung focus on catching up technologically, TSMC’s operational efficiency and cost improvements have enabled it to achieve an impressive gross margin of 57.8%. By comparison, Intel's margin of 43% and Samsung's estimated 38-40% gross margin show how much ground they need to cover to match TSMC's profitability. With TSMC forecasting even higher margins in Q4, its financial strength continues to outshine its competitors.
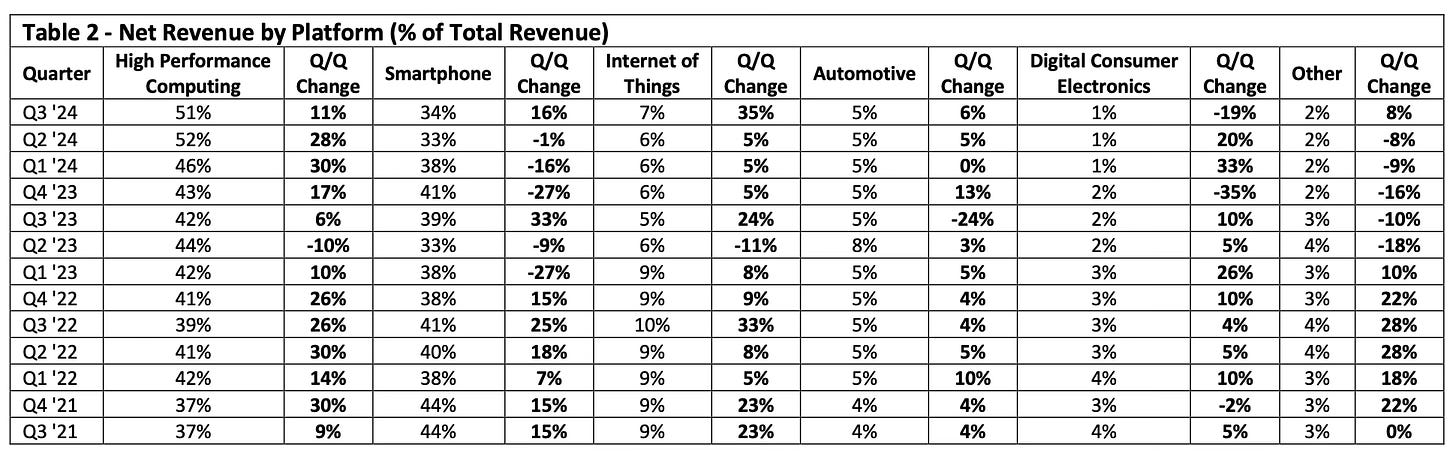
The Shift in Revenue Drivers: Beyond Smartphones
TSMC’s Q3 earnings demonstrate its ability to expand beyond the smartphone sector as shown in Table 2. High-performance computing (HPC) accounted for 51% of total revenue, fueled by strong demand for AI processors and data center chips. Smartphone revenue, while still substantial at 34%, has taken a slight dip as TSMC shifts focus toward more lucrative markets like AI and HPC.
The Internet of Things (IoT) sector showed remarkable growth, with a 35% quarter-over-quarter increase in revenue driven by rising demand for connected devices and smart infrastructure. In contrast, automotive grew by a more modest 6% in Q3, reflecting steady demand for semiconductor components in electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Meanwhile, Intel remains heavily reliant on internal chip production, and Samsung continues to struggle with yield issues that have limited its ability to meet demand in the AI and IoT markets. TSMC’s diversified revenue streams, especially from AI and IoT, further strengthen its position as the industry leader.
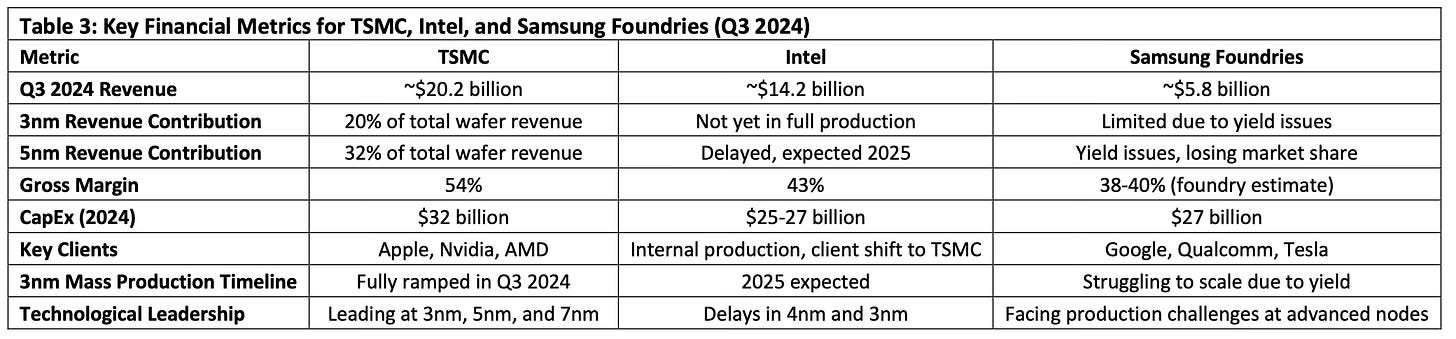
Financial and Technological Comparison: TSMC, Intel, and Samsung
Table 3 presents a clear comparison between TSMC, Intel, and Samsung Foundries in terms of their financial performance and technological capabilities. TSMC’s Q3 revenue of $20.2 billion dwarfs Intel’s $14.2 billion and Samsung’s $5.8 billion. This revenue lead is directly linked to TSMC’s advanced node production, particularly in 3nm and 5nm technologies. In contrast, Intel’s foundry services segment, still in its nascent stages, struggles to gain traction and is far behind TSMC in both revenue and technological readiness.
Gross margin comparisons tell a similar story. TSMC’s gross margin stands at an impressive 54%, reflecting the high demand for its advanced node technology and efficient production processes. Intel’s gross margin is significantly lower at 43%, a sign of the financial strain caused by its delayed 4nm and 3nm nodes. Samsung, too, lags behind with an estimated gross margin of 38-40% in its foundry business, largely due to ongoing yield issues at 5nm and 3nm.
The capital expenditures (CapEx) of these companies reflect their efforts to stay competitive. TSMC’s planned CapEx for 2024 is a staggering $32 billion, primarily focused on expanding capacity for its 3nm and 2nm technologies. Intel’s CapEx of $25-27 billion is similarly large, but much of this investment is focused on playing catch-up, as it ramps up production at its new fabs in Ohio and Germany. Samsung, with a CapEx of $27 billion, is also investing heavily in expanding its foundry operations, but without the same operational efficiencies and technological lead as TSMC.
The technological gap is even more evident when comparing 3nm production timelines. TSMC has already ramped up mass production of its 3nm chips, securing major contracts with Apple and Nvidia, while Intel and Samsung are still struggling to meet yield and production targets. Intel’s 3nm (Intel 3) is expected to enter mass production only in 2025, and Samsung’s 3nm GAA has been plagued by technical difficulties, preventing it from gaining significant market share in this advanced node.
Conclusion: The Gap Widens
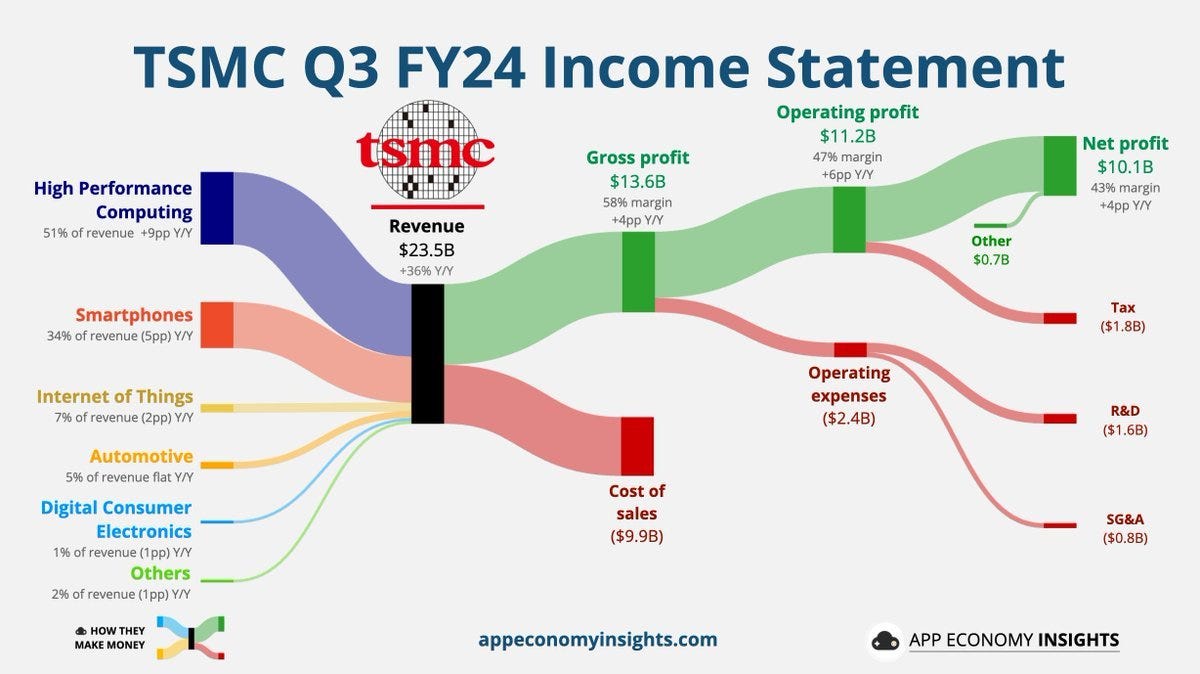
The TSMC Q3 FY24 Income Statement (Chart 1)showcases TSMC's strong financial health and operational efficiency, reporting $23.5 billion in revenue, a 36% year-over-year increase. High-performance computing (HPC) was the largest contributor, making up 51% of total revenue, while smartphones accounted for 34%. With a 58% gross margin, TSMC achieved a $13.6 billion gross profit, while keeping operating expenses, R&D, and SG&A under control. This allowed TSMC to deliver an operating profit of $11.2 billion, reflecting a 47% margin, and a net profit of $10.1 billion at a 43% margin. The company's disciplined approach to managing costs while continuing to invest heavily in R&D ($1.6 billion) and operating expenses ($2.4 billion) underscores its commitment to innovation and leadership in the semiconductor space, all while maintaining impressive profitability.
Chart 1
The Q3 2024 results highlight just how far TSMC has pulled ahead of Intel and Samsung in the semiconductor foundry race. TSMC’s technological prowess at 3nm and 5nm, combined with its ability to rapidly scale production, has allowed it to secure more market share in key sectors such as AI, HPC, and automotive. Meanwhile, Intel’s delays and Samsung’s yield issues have left them struggling to compete.While Intel and Samsung await High-NA EUV, TSMC is already benefiting from its well-established use of current EUV lithography, with fully ramped 3nm production and a clear roadmap toward 2nm by 2025. TSMC is in a better position to handle delays in High-NA EUV because it has already optimized its existing EUV tools for 3nm and 5nm nodes, giving it a head start in chip production at smaller nodes.
TSMC’s reliance on current EUV for its 3nm and 5nm processes means that while the delay in High-NA EUV is important, it does not critically disrupt its production roadmap. With Apple, Nvidia, and AMD securing advanced chips from TSMC, the foundry giant has been able to maintain its technological leadership even as the industry waits for the next breakthrough in lithography.
As TSMC invests heavily in 2nm technology and prepares for future growth, its competitors face an uphill battle. Intel’s foundry services are still years behind, and Samsung’s challenges with advanced nodes show no signs of abating. The Q3 results make one thing clear: TSMC has delivered a knock-out punch, leaving its rivals playing catch-up in a market where time and technology are everything.
I rate TSM a Strong Buy.




Compelling writing, but ...the risk of PRC invading Taiwan, how does that enter the calculous?